Learn C Programming Language
Multidimensional Arrays in C programming
Multidimensional arrays definition
Arrays in C can have multiple subscripts. A common use of multiple-subscripted arrays, which the C standard refers to as multidimensional arrays, is to represent tables of values consisting of information arranged in rows and columns.
To identify a particular table element, we must specify two subscripts:
- The first (by convention) identifies the element’s row.
- The second (by convention) identifies the element’s column.
Tables or arrays that require two subscripts to identify a particular element are called double-subscripted arrays. Multidimensional arrays can have more than two subscripts.
Array with three rows and four columns, so it’s said to be a 3-by-4 array.
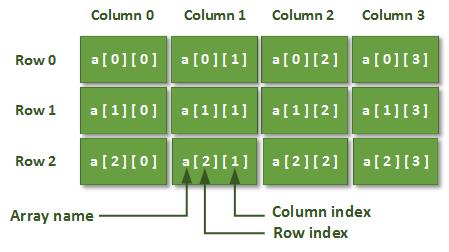
In general, an array with m rows and n columns is called an m-by-n array.
Defining multidimensional array
A multidimensional array can be initialized when it’s defined, much like a single-subscripted array.
Defining a double-subscripted array int b[2][2]:
int b[ 2 ][ 2 ] = { { 1, 2 }, { 3, 4 } };
Initializing multidimensional arrays.
The program defines three arrays of two rows and three columns (six elements each).
- The definition of array1 provides six initializers in two sublists.
- The definition of array2 provides five initializers.
- The definition of array3 provides three initializers in two sublists.
Note: Uninitialized elements are assigned the value 0.
// Initializing multidimensional arrays.
#include <stdio.h>
void printArray( int a[][ 3 ] ); // function prototype
// function main begins program execution
int main( void ) {
// initialize array1, array2, array3
int array1[ 2 ][ 3 ] = { { 1, 2, 3 }, { 4, 5, 6 } };
int array2[ 2 ][ 3 ] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
int array3[ 2 ][ 3 ] = { { 1, 2 }, { 4 } };
puts( "Values in array1 by row are:" );
printArray( array1 );
puts( "Values in array2 by row are:" );
printArray( array2 );
puts( "Values in array3 by row are:" );
printArray( array3 );
} // end main
// function to output array with two rows and three columns
void printArray( int a[][ 3 ] ) {
size_t i; // row counter
size_t j; // column counter
// loop through rows
for ( i = 0; i <= 1; ++i ) {
// output column values
for ( j = 0; j <= 2; ++j ) {
printf( "%d ", a[ i ][ j ] );
} // end inner for
printf( "\n" ); // start new line of output
} // end outer for
} // end function printArray
Output:
Values in array1 by row are:
1 2 3
4 5 6
Values in array2 by row are:
1 2 3
4 5 0
Values in array3 by row are:
1 2 0
4 0 0
Ads Right

