Learn C Programming Language
Arrays in C programming
Arrays
An array is a group of contiguous memory locations that all have the same type. To refer to a particular location or element in the array, we specify the array’s name and the position number of the particular element in the array.
The first element in every array is the zero element. An array name, like other variable names, can contain only letters, digits and underscores and cannot begin with a digit.
Example of an integer array called a, containing 8 elements:
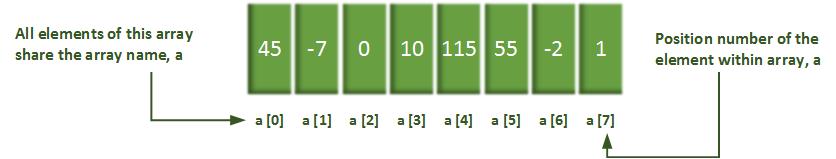
Defining array
Arrays occupy space in memory. You specify the type of each element and the number of elements each array requires so that the computer may reserve the appropriate amount of memory.
Array a reserves 12 integer elements, which has subscripts in the range 0–11.
int a[ 12 ];Array example
Initializing an Array in a Definition with an Initializer List
The elements of an array can also be initialized when the array is defined by following the definition with an equals sign and braces, {}, containing a comma-separated list of array initializers.
// Initializing the elements of an array with an initializer list.
#include <stdio.h>
// function main begins program execution
int main( void )
{
// use initializer list to initialize array n
int n[ 10 ] = { 32, 27, 64, 18, 95, 14, 90, 70, 60, 37 };
size_t i; // counter
printf( "%s%13s\n", "Element", "Value" );
// output contents of array in tabular format
for ( i = 0; i < 10; ++i ) {
printf( "%7u%13d\n", i, n[ i ] );
} // end for
} // end main
Output:
Element Value
0 32
1 27
2 64
3 18
4 95
5 14
6 90
7 70
8 60
9 37
Using Character Arrays to Store and Manipulate Strings
Character arrays have several unique features. A character array can be initialized using a string literal.
char string1[] = "hello";
The example above initializes the elements of array string1 to the individual characters in the string literal "hello". In this case, the size of array string1 is determined by the compiler based on the length of the string.
The string "hello" contains five characters plus a special string-termination character called the null character.
// Treating character arrays as strings.
#include <stdio.h>
#define SIZE 20
// function main begins program execution
int main( void ) {
char string1[ SIZE ]; // reserves 20 characters
size_t i; // counter
// read string from user into array string1
printf( "%s", "Enter a string (no longer than 19 characters): " );
scanf( "%19s", string1 ); // input no more than 19 characters
// output string, and its length
printf( "string1 is: %s\n"
"string1 size is: %ld\n"
"string1 with spaces between characters is: ", string1
,strlen(string1));
// output characters until null character is reached
for ( i = 0; i < SIZE && string1[ i ] != '\0'; ++i ) {
printf( "%c ", string1[ i ] );
} // end for
puts( "" );
} // end main
Output:
Enter a string (no longer than 19 characters): infocode
string1 is: infocodes
string1 size is: 9
string1 with spaces between characters is: i n f o c o d e s
Ads Right

